IONIC EQUILIBRIA - Notes : Class 12th Chemistry Chapter 3 : Maharashtra State Board New Syllabus : Free Net Notes
Maharashtra State Board New Syllabus - Chemistry Chap 3 - Ionic Equilibria
Notes, Important Points, Definitions, Formulae..
Introduction
What is Ionic Equilibrium ?
Answer -
Definition : - The equilibrium between ions and unionized molecules in solution is called ionic equilibrium.
Example : -
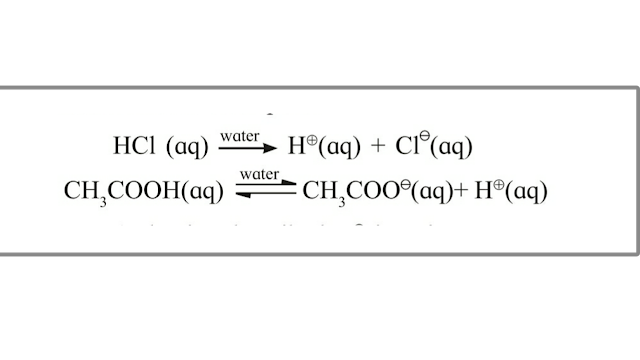
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ CH3COO- (aq)+ H⊕ (aq)
GENERAL FORM - AB ⇌ A+ + B–
What is an Electrolyte & a Non-Electrolyte ?
Answer -
Definition Electrolyte : - The substances which give rise to ions when dissolved in water are electrolytes.
Definition Non-Electrolyte : - The non electrolytes are those which do not ionize and exist as molecules in aqueous solutions.
CLASSIFICATION OF ELECROLYTE BASED ON - Extent of Ionisation in Dilute Aqueous Solutions
Strong Electrolyte -
Definition : - The electrolytes ionizing completely or almost completely are strong electrolytes.
Example : - strong acids, strong bases and salts.
Weak Electrolyte -
Definition : - The electrolytes which dissociate to a smaller extent in aqueous solution are weak electrolytes.
Note : An equilibrium is established between ions and unionized molecules (ionic equilibrium) when weak electrolyte is added in aqueous solutions.
Example : - Weak acids and weak bases.
Degree of Dissociation
Definition : The degree of dissociation of an electrolyte is defined as a fraction of total number of moles of the electrolyte that dissociates into its ions when the equilibrium is attained.
Denoted by - ∝ (alpha)
ACIDS AND BASES
Arrhenius Theory of Acids and Bases : -
Definitions According to Arrhenius : -
Acid : Acid is a substance which contains hydrogen and gives rise to H⊕
ions in aqueous
solution.
Base : Base is a substance that contains OH group and produces hydroxide ions (OH ) ions in aqueous solution.
Limitations of Arrhenius Theory :-
- It is applicable only to aqueous solutions.
- It does not account for basicity of NH3 and Na2CO3 which do not have OH group.
Bronsted-Lowry Theory ( Bronsted-Lowry Proton Transfer Theory )
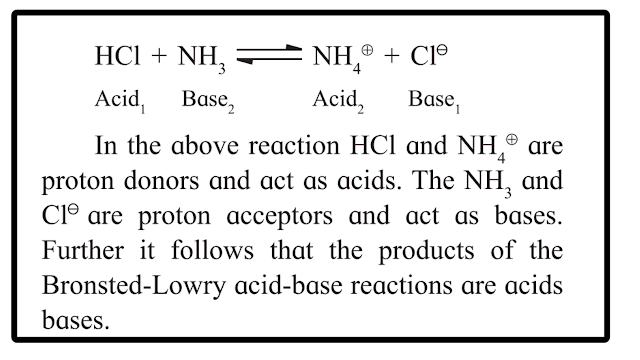
Acid : Acid is a substance that donates a proton (H+) to another substance .
Base : Base is a substance that accepts a proton (H+) from another substance .
Conjugate Base : The base produced by accepting the proton from an acid is the conjugate base of that acid.
Conjugate Acid : The acid produced when a base accepts a proton is called the conjugate acid of that base.
Conjugate Acid-Base Pair : A pair of an acid and a base differing by a proton is said to be a conjugate acid-base pair.
Lewis Theory
Acid : Any species that accepts a share in an electron pair is called Lewis Acid.
Base : Any species that donates a share in an electron pair is called Lewis Base.
Amphoteric Nature of Water : Water has the ability to act as an acid as well as a base. Such behaviour is known as amphoteric nature of water.
Ionisation of Acids and Bases.
CLASSIFICATION OF ACIDS AND BASES ARE BASED ON THEIR EXTENT OF DISSOCIATION
: -
Here are some examples of strong acids, strong bases , weak acids and weak bases.
1) Strong Acids :- EXAMPLE - HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, HBr AND HI
2) Strong Bases :- EXAMPLE - NaOH AND KOH.
3) Weak Acids : - EXAMPLE - HCOOH, HF, H2S
4) Weak Bases :- EXAMPLE - Fe(OH)3, Cu(OH)
Note :
1) Stong acids and Strong bases are almost completely dissociated in water.
2) Weak Acids and weak bases are partially dissociated in water.
Dissociation costant for Weak Acids and Weak Bases
Defination : The dissociation constant of a weak acid or weak base is defined as the equilibrium constant for dissociation equilibrium of weak acid or weak base , respectively.
Ostwald's Dilution Law :-







Sir full chapter kab aayaga
ReplyDeletefull lesson will be uploaded soon
DeleteOkay sir🙂🙂🙂
Deletefull lesson uploaded quickly sir 👍
DeletePlease upload as soon as possible we all needed this....
DeletePlease send full chapter notes
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
Deleteaur notes kab ayenge sir
ReplyDeleteremaining ?
ReplyDeleteAs fast as possible please upload the remained part of the chapter
ReplyDeleteSir plz upload remaining part
ReplyDeleteSir please upload remaing part
ReplyDeleteSir please upload remaining part of chapter
ReplyDeleteSend full
ReplyDeleteChapter notes please sir
Please send a remaining part of this chapter
ReplyDeleteSir please quickly send the notes of remaining part of the chapter
ReplyDeleteSir please upload remaining part
ReplyDeleteFull chapter notes
ReplyDeleteSir please upload remaining notes
ReplyDeletePlease aplod the remaining part notes of this chapter
ReplyDeleteSir please send remaining notes of this lesson 🙂
ReplyDeleteSir please send remaining notes for this lesson 🙏
ReplyDeleteSir please send full notes
ReplyDeleteSir plz send full notes
ReplyDeletesir send the full chapter notes please please please🙏🙏🙏🙏😊😊
ReplyDeleteSir plz send full notes
ReplyDeleteSir full notes patvana
ReplyDeleteSir full notes .... bhejo na
ReplyDeleteSir full chapter
ReplyDeleteRemaining notes???
ReplyDelete